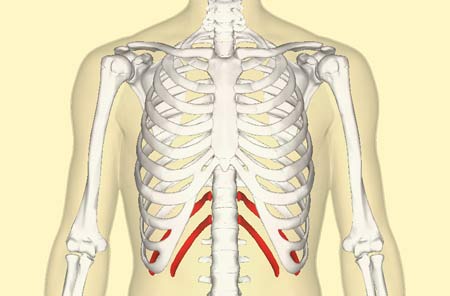
 I`m not a huge fan of the term “floating rib,” it implies that the rib is just floating around in the abdomen and not doing much. In reality, these set of ribs are heald in place by numerous attachments, even though they are not directly attached to the sternum.
I`m not a huge fan of the term “floating rib,” it implies that the rib is just floating around in the abdomen and not doing much. In reality, these set of ribs are heald in place by numerous attachments, even though they are not directly attached to the sternum.
There aren`t a lot of “disorders” commonly affecting these ribs, but there is one which can cause pain in the floating rib area and its called Floating Rib or a Slipped Rib Syndrome. Another common cause of pain in this area is an injury.
What Is A Floating Rib And What Does It Do?
Sure, we`ve all heard of “regular” ribs, a long, curved bone which attaches to the spine, at the back, and to the sternum, at the front; but a floating rib only attaches to the spine and not the sternum.
In total, there are 12 pairs of ribs in our rib cage:
- True Ribs – 1-7 attached to spine and sternum via costal cartilage
- False Ribs – 8-10 attached to the spine and costal cartilage of the seventh rib (not directly to sternum) and
- Floating ribs – 11-12 attached to the spine only
Though most people have two pair of floating ribs, some may have only one or as much as three.
The precise function of these ribs is still a sort of a mystery, but the current theory is that they provide a bit of extra protection to the internal organs. As you can see for yourself, this is not the best or the most viable theory, so some speculate that these ribs are remnants of some earlier stage in our evolution.
In any case, their function is not 100% clear but they can cause certain health problems. And we are going to discuss them in the following section.
Floating Rib Syndrome
 Though some author`s make the distinction between floating and slipped rib syndrome, they are basically the same. Other common names for it are slipping rib cartilage, nerve nipping, clicking ribs and rib-tip syndrome. This syndrome is less widely known, so identifying it and diagnosing might be a bit tricky.
Though some author`s make the distinction between floating and slipped rib syndrome, they are basically the same. Other common names for it are slipping rib cartilage, nerve nipping, clicking ribs and rib-tip syndrome. This syndrome is less widely known, so identifying it and diagnosing might be a bit tricky.
The best way to diagnose this condition is to do a manual palpation or by hooking the fingers under the ribs and pulling forward. It is also not that uncommon to ask for an X-ray of the affected area to check the correct position of the ribs.
The main characteristic and symptom of floating rib syndrome is, of course, the pain. Patients suffering from it feel the pain at the front of the floating ribs, which intensifies with movement or deep breathing. The pain is usually localized on the left or the right and can vary from a mild ache to sharp, stabbing sensation of pain spreading across the rib cage and abdominal wall.
The most common cause of this syndrome is a traumatic injury. Patients will usually recall some sort of an injury after which they started to experience pain.
Treatment
There is no specially designed treatment for this condition. It is usually enough just to recognize it and administer a proper use of analgesics. Doctor might also instruct the patient to avoid and movement or positions which will intensify the pain.
In more severe cases, (more severe injuries) partial immobilization might be required. And if the rib pops out of its socket and becomes dislocated, physical adjusting and manipulation will help correct its position and return the patient back to normal.
The pain usually lasts for several months before healing completely.
References:

i would like to e-mail this article to a friend. how do i do that
Hi Cheryl,
The best way to do so would be to copy the URL of the article ( http://helpyourback.org/health/floating-rib-syndrome-is-probably-causing-your-rib-pain ) and send that to your friend.
Regards,
Igor
Great article. Very informative. Exactly what I have.